ANOVA Analysis of Variance is a statistical test used to analyze the difference between the means of more than two groups. The two-way ANOVA is probably the most popular layout in theDesign of Experiments. A two way anova means that the experimental design includes
A Two Way Anova Means That The Experimental Design Includes, The effect of one independent variable depends on the levels of the second variable. A two-way ANOVA has three null hypotheses three alternative hypotheses and three answers to the research question. Completely randomized design with treatments randomly assigned to the g. Design of experiment means how to design an experiment in the sense that how the observations or measurements should be obtained to answer a query in a valid efficient and economical way.
 Two Way Anova When And How To Use It With Examples From scribbr.com
Two Way Anova When And How To Use It With Examples From scribbr.com
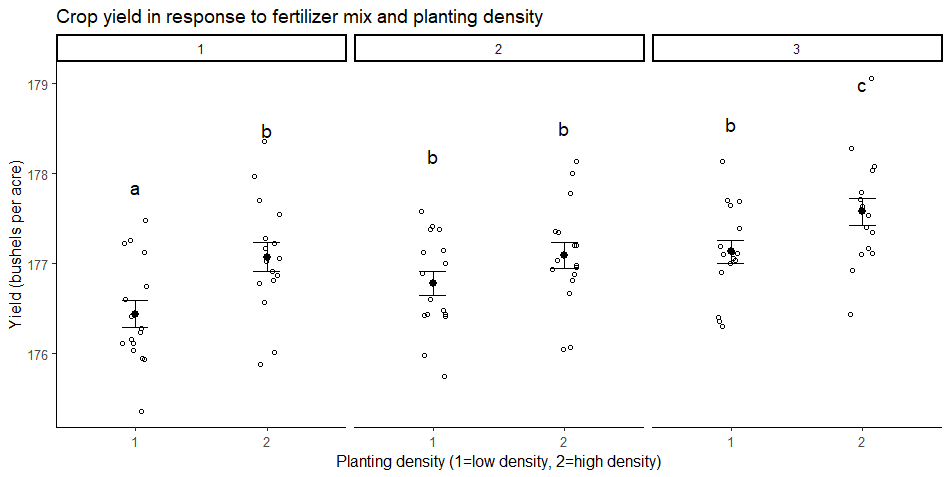
Are walruses heavier in early or late mating season and does that depend on the sex of the walrus. Y is a quantitative response variable There are two categorical explanatory variables called Factors. An experiment that utilizes every combination of factor levelsas treatments is called a factorial experiment. Two grouping variables we sometimes refer to the analysis as a two-way ANOVA in contrast to the one-way ANOVAs that we ran in Chapter 12.
Two grouping variables we sometimes refer to the analysis as a two-way ANOVA in contrast to the one-way ANOVAs that we ran in Chapter 12.
Read another article:
Subsequently question is what is in an experimental design. More complex experimental designs classically analyzed with. One or More Independent Variables With Two or More Levels Each and More Than One Dependent Variable. A two factor experiment means that the experimental design includes. The denominator of the f-ratio.
 Source: scribbr.com
Source: scribbr.com
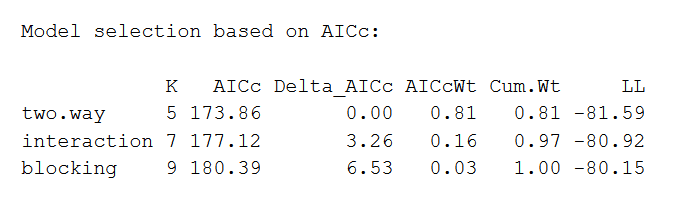
Experimental design refers to how participants are allocated to the different conditions or IV levels in an experiment. In a matrix for a factorial design the row means and column means represent the effects of a singe factor variable. Emphasis will be placed on important design-related concepts such as randomization blocking factorial design and causality. Subsequently question is what is in an experimental design. Two Way Anova When And How To Use It With Examples.
 Source: spss-tutorials.com
Source: spss-tutorials.com
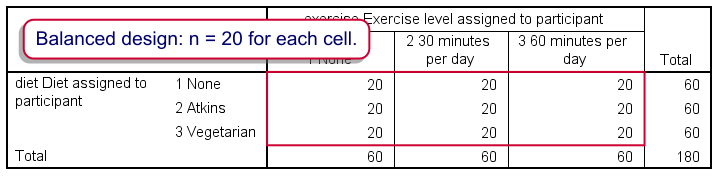
A two-way ANOVA is an extension of the one-way ANOVA analysis of variances that reveals the results of two independent variables on a dependent variable. Emphasis will be placed on important design-related concepts such as randomization blocking factorial design and causality. If an experiment has a quantitative outcome and two categorical explanatory variables that are de ned in such a way that each experimental unit subject can be exposed to any combination of one level of one explanatory variable and one. In a matrix for a factorial design the row means and column means represent the effects of a singe factor variable. Spss Two Way Anova Quick Tutorial.
 Source: technologynetworks.com
Source: technologynetworks.com
The two-way ANOVA is probably the most popular layout in theDesign of Experiments. Subsequently question is what is in an experimental design. The effect of one independent variable depends on the levels of the second variable. In the two-way ANOVA model there are two factors each with several levels. One Way Vs Two Way Anova Differences Assumptions And Hypotheses Technology Networks.
 Source: dzchilds.github.io
Source: dzchilds.github.io
The primary purpose of a two-way ANOVA is to understand if there is an interaction between the two independent variables on the dependent variable. An experiment that utilizes every combination of factor levelsas treatments is called a factorial experiment. If the model has a single categorical factor and one continuous factor it is an ANCOVA short for analysis of covariance next chapter. As in one-way ANOVA the data for a two-way ANOVA study can be experimental or observational. Chapter 27 Two Way Anova In R Aps 240 Data Analysis And Statistics With R.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The denominator of the f-ratio. As in one-way ANOVA the data for a two-way ANOVA study can be experimental or observational. The designing of the experiment and the analysis of obtained data are inseparable. 131 Factorial ANOVA 1. Detailed And Helpful Compare Contrast Between Other Methods Cause And Effect What Is Meant Compare And Contrast.
 Source: biostathandbook.com
Source: biostathandbook.com
To begin withlet us define a factorial experiment. An experiment that utilizes every combination of factor levelsas treatments is called a factorial experiment. Emphasis will be placed on important design-related concepts such as randomization blocking factorial design and causality. Level of a factor p. Two Way Anova Handbook Of Biological Statistics.
 Source: scribbr.com
Source: scribbr.com
Y is a quantitative response variable There are two categorical explanatory variables called Factors. 131 Factorial ANOVA 1. Design of experiment means how to design an experiment in the sense that how the observations or measurements should be obtained to answer a query in a valid efficient and economical way. When we are interested in the effects of two factors a two-way design offers great advantages over two single-factor studies. Two Way Anova When And How To Use It With Examples.
 Source: scribbr.com
Source: scribbr.com
Factor A has K levels k 1 K Factor B has J levels j 1 J. Model for the two-way factorial experiment. 131 Factorial ANOVA 1. Y is a quantitative response variable There are two categorical explanatory variables called Factors. A Quick Guide To Experimental Design 5 Steps Examples.
 Source: spss-tutorials.com
Source: spss-tutorials.com
The answers to the research questions are similar to the answer provided for the one-way ANOVA only there are three of them. A two-way ANOVA has three null hypotheses three alternative hypotheses and three answers to the research question. The effect of one independent variable depends on the levels of the second variable. Adantav ges of two-wy aANOVA. Spss Two Way Anova Quick Tutorial.
 Source: technologynetworks.com
Source: technologynetworks.com
Published on March 20 2020 by Rebecca Bevans. The effect of one independent variable depends on the levels of the second variable. Factor A has K levels k 1 K Factor B has J levels j 1 J. In a matrix for a factorial design the row means and column means represent the effects of a singe factor variable. One Way Vs Two Way Anova Differences Assumptions And Hypotheses Technology Networks.
 Source: keydifferences.com
Source: keydifferences.com
ANOVA Analysis of Variance is a statistical test used to analyze the difference between the means of more than two groups. Y is a quantitative response variable There are two categorical explanatory variables called Factors. The two-way ANOVA is probably the most popular layout in theDesign of Experiments. In a matrix for a factorial design the row means and column means represent the effects of a singe factor variable. Difference Between One Way And Two Way Anova With Comparison Chart Key Differences.
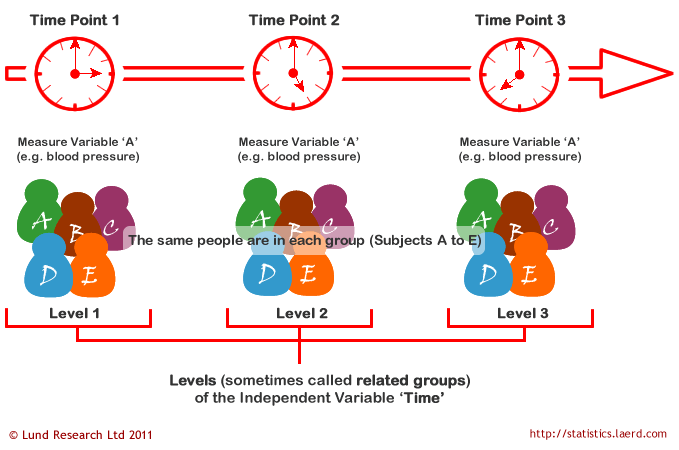 Source: statistics.laerd.com
Source: statistics.laerd.com
An experiment that utilizes every combination of factor levelsas treatments is called a factorial experiment. The answers to the research questions are similar to the answer provided for the one-way ANOVA only there are three of them. Model for the two-way factorial experiment. As in one-way ANOVA the data for a two-way ANOVA study can be experimental or observational. Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics.
 Source: scribbr.com
Source: scribbr.com
131 Factorial ANOVA 1. However in the two-way ANOVA each sample is defined in two ways and resultingly put into two categorical groups. Completely randomized design with treatments randomly assigned to the g. In a matrix for a factorial design the row means and column means represent the effects of a singe factor variable. Two Way Anova When And How To Use It With Examples.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Subsequently question is what is in an experimental design. In one-way ANOVA we classify populations according to one categorical variable or factor. When we are interested in the effects of two factors a two-way design offers great advantages over two single-factor studies. A two-way ANOVA has three null hypotheses three alternative hypotheses and three answers to the research question. How Do I Report A 1 Way Between Subjects Anova In Apa Style Research Methods Advanced Mathematics Anova.
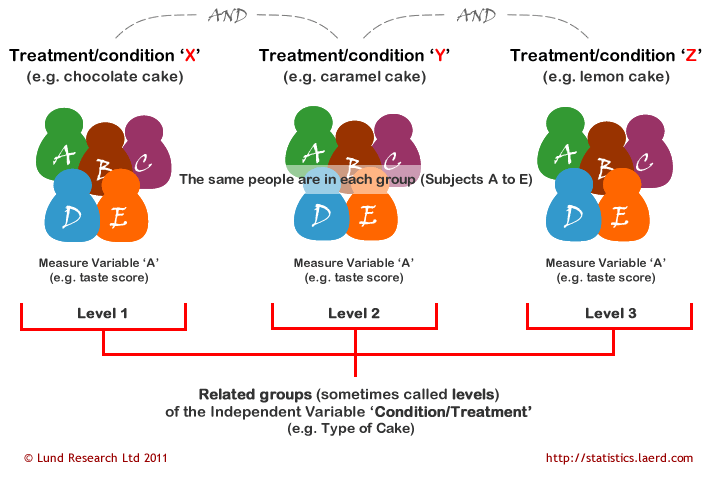 Source: statistics.laerd.com
Source: statistics.laerd.com
In one-way ANOVA we classify populations according to one categorical variable or factor. One or More Independent Variables With Two or More Levels Each and More Than One Dependent Variable. When we are interested in the effects of two factors a two-way design offers great advantages over two single-factor studies. A with a levels and B with b levels. Repeated Measures Anova Understanding A Repeated Measures Anova Laerd Statistics.







